
Contribution Calculators
PSPP is designed to consider the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) contributions using an integrated formula. This is why there is a lower contribution rate and a higher contribution rate.
Jump to Prescribed Contribution Rates.
Calculation Variables
Contributions to the Plan are calculated on a per pay period basis using:
- Pensionable Salary
- Salary cap
- Yearly maximum pensionable earnings (YMPE)
- Prescribed contribution rates
Pensionable Salary
Pensionable salary is the portion of members’ salary on which pension contributions are made. The pensionable salary for PSPP must include gross basic pay, retroactive salary changes, vacation pay (paid time off while employed), and vacation pay (paid as a percentage of salary) as pensionable salary.
Employers can choose to include shift work premiums, weekend work premiums and acting pay as pensionable salary which must be documented in the employer’s Pension Policy.
Lump sum holiday and vacation pay, overtime, special pay/bonuses, severance pay, and expense allowances are non-pensionable. In addition, employer paid remuneration in the form of a top-up to remuneration received from a third party is not considered Pensionable Earnings
| Pensionable Salary | Subject to Employer Policy | Non-pensionable Salary |
|---|---|---|
| Gross basic pay | Shift work premium | Lump sum holiday and vacation pay |
| Retroactive salary changes | Weekend work premium | Overtime |
| Vacation pay (paid time off while employed) | Acting pay | Special pay/Bonuses |
| Vacation pay (paid as a percentage of salary) | Severance Pay | |
| Expense allowance | ||
| Employer paid top up to third party remuneration |
Salary Cap
The federal Income Tax Act (ITA) establishes a defined benefit accrual limit for each year of pensionable service occurring after December 31, 1991. A maximum salary cap is set by the plan rules to ensure member’s benefits do not exceed the ITA’s defined benefit limit.
Contributions to PSPP are only required on pensionable salary up to the salary cap. Even though contributions are deducted from pensionable salary up to salary cap, the member’s full pensionable salary must be reported. This is because it is used in the benefit formula’s calculation of the highest 5-year average salary. Read more about the PSPP benefit formula here.
YMPE
CPP contribution premiums are based off the YMPE which is set by the Federal Government each year. Because members contribute to CPP on pensionable salary up to the YMPE, PSPP has a lower contribution rate on pensionable salary up to the YMPE, and a higher contribution rate for pensionable salary (up to the salary cap) over the YMPE.
Prescribed Contribution Rates
| Member and Employer Contribution Rates | |
|---|---|
| Rate on salary up to YMPE | 8.3% |
| Rate on salary over YMPE (up to the salary cap) | 11.9% |
Contribution Calculation Steps
Full-time Pay Period Calculation Steps
Contributions are calculated on a per pay period basis, so calculation variables need to be determined on a per pay period basis. See examples here.
- Determine pay period pensionable salary.
- Determine pay period YMPE. This is calculated by dividing the YMPE by the number of pay periods in a year.
- Determine pay period salary cap. This is calculated by dividing the salary cap by the number of pay periods in a year.
- Determine pensionable salary for the lower rate (up to the YMPE).
- Determine pensionable salary for the higher rate (over the YMPE and up to the salary cap if applicable).
- Calculate lower rate contributions and higher rate contributions using the prescribed contribution rates.
Part-Time or Partial Pay Period Calculation Steps
Pay period contributions are calculated on an annualized basis for part-time members and for members working a partial pay period. This means that the pay period pensionable salary is annualized then contributions are prorated by the Full-Time Equivalent service (FTE) as described below. See steps and examples here.
Full-time Member Examples
The 2025 YMPE is set at $71,300 and the salary cap is $209,223.50.
Example 1 – the member makes $75,000 annually and is paid on a bi-monthly basis with 24 pay periods within a year.
1. Pay period pensionable salary = $3,125
2. Pay period YMPE: $71,300/24 = $2,970.83
3. Pay period salary cap: 209,223.50/24 = $8,717.65 (N/A)
4. Pensionable salary for lower rate calculation: $2,970.83
5. Pensionable salary for higher rate calculation: $3,125 – $2,970.83 = $154.17
6. Calculate lower rate contributions: $2,970.83 x 8.3% = $246.58; calculate higher rate contributions: $154.17 x 11.9% = $18.35. The total is $264.93
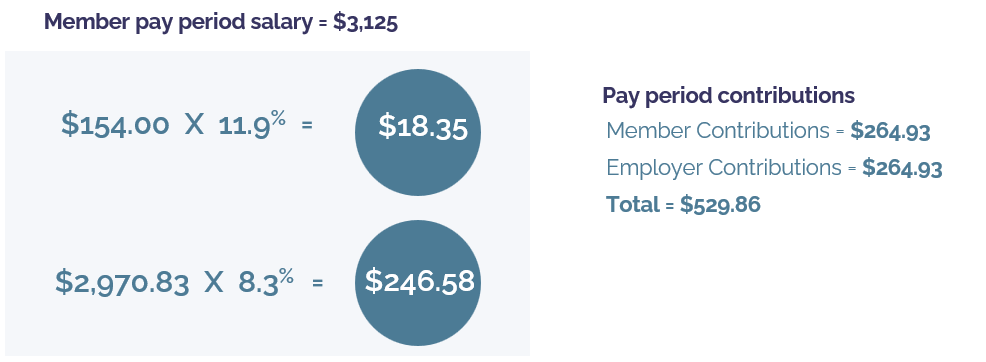
Example 2 – the member makes $60,000 annually and is paid on a bi-weekly basis with 26 pay periods in a year.
1. Pay period pensionable salary = $2,307.69
2. Pay period YMPE: $71,300/26 = $2,742.31
3. Pay period salary cap: 209,223.50/24 = $8,717.65 (N/A)
4. Pensionable salary for lower rate calculation: $2,307.69
5. Pensionable salary for higher rate calculation: $0.00 (N/A)
6. Calculate lower rate contributions: $2,307.69 x 8.3% = $191.54; calculate higher rate contributions: $0.00. The total is $191.54

Example 3 – the member makes $208,000 annually and is paid on a monthly basis with 12 pay periods in a year.
1. Pay period pensionable salary = $17,333.33
2. Pay period YMPE: $71,300/12 = $5,941.67
3. Pay period salary cap: 209,223.50/12 = $17,435.29 (N/A)
4. Pensionable salary for lower rate calculation: $5,941.67
5. Pensionable salary for higher rate calculation: $17,435.29-$5,941.67 = $11,493.63
6. Calculate lower rate contributions: $5,941.67 x 8.3% = $493.16; calculate higher rate contributions: $11,493.63*11.9% = $1,367.74 The total is $1,860.90
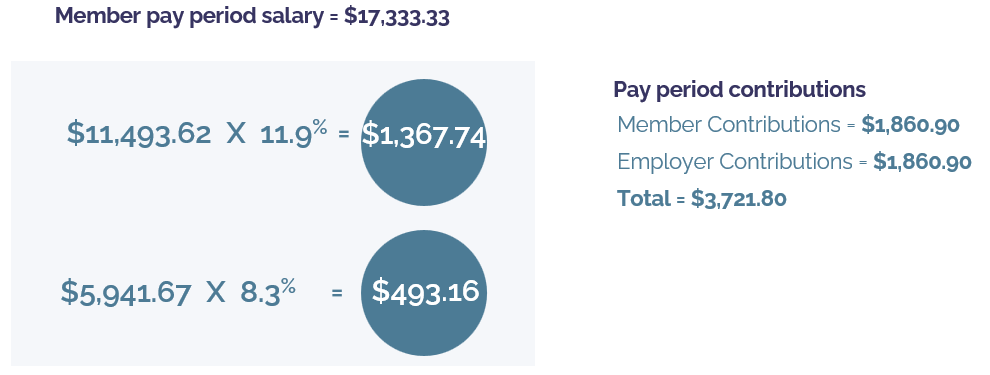
Part-Time or Partial Pay Period Examples
Pay period contributions are calculated on an annualized basis for part-time members and for members working a partial pay period. This means that the pay period pensionable salary is annualized when contributions are prorated by the Full-Time Equivalent service (FTE) as described in the examples.
- Determine the annualized pay period pensionable salary by dividing the member’s salary by FTE service.
- Determine pay period YMPE by dividing the YMPE by the number of pay periods in a year.
- Determine pay period salary cap by dividing the salary cap by the number of pay periods in a year.
- Determine annualized pensionable salary for the lower rate (up to the YMPE).
- Determine annualized pensionable salary for the higher rate (over the YMPE and up to the salary cap if applicable).
- Calculate lower rate contributions and higher rate contributions using the prescribed contribution rates.
- Prorate the contributions calculated on the annualized earnings by multiplying the annualized pay-period contributions by the FTE (Part-time or less than full-time service).
The 2025 YMPE is set at $71,300 and the salary cap is $209,223.50.
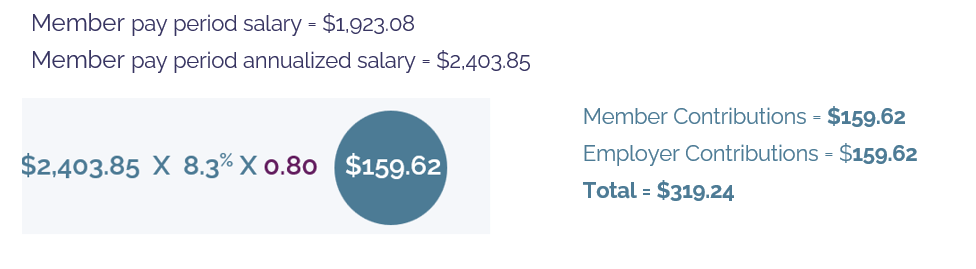
Example 1 – the member makes $50,000 annually and is paid on a bi-weekly basis with 26 pay periods in a year. The member works a 0.80 FTE and has no leave of absence.
1. Annualized pay period pensionable salary = $1,923.08/0.80 = $2,403.85
2. Pay period YMPE: $71,300/26 = $2,742.31
3. Pay period salary cap: $209,223.50 /26 = $8,047.06 (N/A)
4. Pensionable salary for lower rate calculation: $2,403.85
5. Pensionable salary for higher rate calculation: N/A
6. Calculate lower rate contributions: $2,403.85 x 8.3% x 0.80= $159.62
Example 2 – the member makes $63,200 annually and is paid on a bi-weekly basis with 26 pay periods in a year. The member works a 0.80 FTE and has no leave of absence.
1. Annualized pay period pensionable salary = $2,430.77/0.80=$3,038.46
2. Pay period YMPE: $71,300/26 = $2,742.31
3. Pay period salary cap: $209,223.50 /26 = $8,047.06 (N/A)
4. Pensionable salary for lower rate calculation: $2,742.31
5. Pensionable salary for higher rate calculation: $3,038.46 – $2,742.31 = $296.15
6. Calculate lower rate contributions: $2,742.31 x 8.3% x0.80= $182.09; calculate higher rate contributions: $296.15 x 11.9% x 0.80 = $28.19 the total is $210.28
